Internet Of Things: Creating Efficiencies Across Industries
IoT is about digitisation of assets in a manner in which they can then communicate with each other like onewould in the online digital space of information. This allows for a huge generation of data and also the possibility of Leveraging this data to make life easier and more connected. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers(IEEE) took on the task of reviewing definitions created by various organisations and individuals and created a definition of IoT. “An IoT is a network that connects uniquely identifiable ‘Things’ to the Internet. The ‘Things’ have sensing/actuation and potential programming capabilities. Through the exploitation of unique identification and sensing, information about the ‘Thing’ can be collected and the state of the ‘Thing’ can be changed from any where, anytime, by anything”.
The fourth Industrial revolution(Industry 4.0) is upon us;the figure below illustrates the progression of this revolution. This development is being led by the Internet of Things (IoT) which is leveraging the internet and computing infrastructure to connect machines, appliances and people.
Technology transformations involving large scale deployment of IoT can translate into business opportunities. Some of the trends which may emerge would be:
1.Higher operational efficiencies
2.New connected ecosystems around software platforms
3.Greater collaboration between humans and machines
4.Shift from selling products and services to selling measurable outcomes
Industry stalwarts have a very optimistic view of the IoT opportunity and some estimates suggest that around 50 billion assets will be connected to the internet by 2020 and the investment would top 60 trillion dollars during next 15 years. Sensors, control systems, feedback loops, internet, AI and other components have been around for a long time but IoT has only gained currency in the recent past. Some of the drivers of this growth include the following:
1.Availability of inexpensive and high-power chips driven due to the high volumes in the cell phone industry. A
wide variety of sensors like accelerometers, cameras, temperature are now available at sharply lower price points
2.Standardization of the protocols like TCP/IP and of address ability of large number of devices using IPv6
3.Standardization and maturity of software technologies including artificial intelligence, cloud computing and cyber security. Rapid adoption of cloud computing is providing Infrastructure as a Service(IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service(SaaS) in a consolidated and cost effective manner. Smart devices and services using AI technologies in the consumer space like Alexa, Siri, Face recognition, Algorithm based financial advisor and others are rapidly being adopted in the consumer space leading to diffusion of this technology to other domains.
"Start small and develop projects to build experience and confidence, develop pilots, focus on asset monitoring across single asset type like high voltage or medium voltage grids"
Earlier cost of IoT solution was high but due to above there has been a significant reduction in cost and increase in performance which has led to a sustained emergence of IoT.
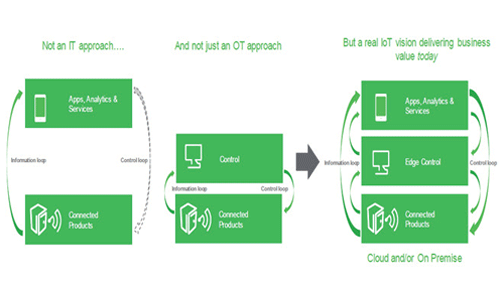
IoT is characterized by the convergence of enterprise ICT (IT) and operational technology(OT). The two systems have been merged and leveraged in a meaningful way to realize fully the objectives of the business. Enterprise IT helps to manage the value chain, reduce cost and improve customer service through huge advances in resource planning, customer relationships, management, decision support systems etc. Operational technology (OT) has been in use for improving yield, quality and efficiency through its use in factory and process automation. Operational technologies like PLC, SCADA, Process Automation etc. are being widely used.
The Internet of Things – Solution Architecture
A typical solution architecture contains these components Connected Products, Edge control, Apps, Analytics and services. Apart from the first two components the IoT industry has standardized on a cloud based PaaS architecture for the remaining components. IBMBluemix- IoT, Microsoft Azure-IoT and SAP HANA-IoT, Schneider Electric – EcoStruxure are examples of PaaS customized for IoT. A typical PaaS with six Architectures from Schneider electric is shown in the picture.
Along with the promises which IoT brings there are some challenges too in the adoption of IoT and the key ones include, among others, financial constraints - often large investments could be required to modernise the energy infrastructure and achieve the benefits of IoT. A possible way forward could be to start small and develop projects to build experience and confidence, develop pilots, focus on asset monitoring across single asset type like high voltage or medium voltage grids. Another challenge could be the lack of availability of skills for realising the full benefits of IoT, however in India we already have a large pool of people in IT and OT industry and it will be easy for them to add additional skills which will help them scale up in the IoT driven world. This will help gain higher efficiencies and reliability keeping the overall cost low. The way forward would be to have capacity building and knowledge transfer as focus areas. This will ensure that skill development is an essential part of the transformation.
2.Standardization of the protocols like TCP/IP and of address ability of large number of devices using IPv6
3.Standardization and maturity of software technologies including artificial intelligence, cloud computing and cyber security. Rapid adoption of cloud computing is providing Infrastructure as a Service(IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service(SaaS) in a consolidated and cost effective manner. Smart devices and services using AI technologies in the consumer space like Alexa, Siri, Face recognition, Algorithm based financial advisor and others are rapidly being adopted in the consumer space leading to diffusion of this technology to other domains.
"Start small and develop projects to build experience and confidence, develop pilots, focus on asset monitoring across single asset type like high voltage or medium voltage grids"
Earlier cost of IoT solution was high but due to above there has been a significant reduction in cost and increase in performance which has led to a sustained emergence of IoT.
IoT is characterized by the convergence of enterprise ICT (IT) and operational technology(OT). The two systems have been merged and leveraged in a meaningful way to realize fully the objectives of the business. Enterprise IT helps to manage the value chain, reduce cost and improve customer service through huge advances in resource planning, customer relationships, management, decision support systems etc. Operational technology (OT) has been in use for improving yield, quality and efficiency through its use in factory and process automation. Operational technologies like PLC, SCADA, Process Automation etc. are being widely used.
The Internet of Things – Solution Architecture
A typical solution architecture contains these components Connected Products, Edge control, Apps, Analytics and services. Apart from the first two components the IoT industry has standardized on a cloud based PaaS architecture for the remaining components. IBMBluemix- IoT, Microsoft Azure-IoT and SAP HANA-IoT, Schneider Electric – EcoStruxure are examples of PaaS customized for IoT. A typical PaaS with six Architectures from Schneider electric is shown in the picture.
Along with the promises which IoT brings there are some challenges too in the adoption of IoT and the key ones include, among others, financial constraints - often large investments could be required to modernise the energy infrastructure and achieve the benefits of IoT. A possible way forward could be to start small and develop projects to build experience and confidence, develop pilots, focus on asset monitoring across single asset type like high voltage or medium voltage grids. Another challenge could be the lack of availability of skills for realising the full benefits of IoT, however in India we already have a large pool of people in IT and OT industry and it will be easy for them to add additional skills which will help them scale up in the IoT driven world. This will help gain higher efficiencies and reliability keeping the overall cost low. The way forward would be to have capacity building and knowledge transfer as focus areas. This will ensure that skill development is an essential part of the transformation.
